Backup and restore#
Caution
Open a support ticket to get assistance from Anaconda if you are upgrading your operating system or plan on migrating your instance of Package Security Manager to a new operating system architecture, as this could severely impact your Package Security Manager instance!
Prerequisites#
pg_dump version 9.6.4+
pg_restore version 9.6.4+
Linux’s open file maximum must be set to 300,000
Increasing the Open File Limit in Linux
To increase the number of files that are allowed to be open at once in Linux, run the following command:
sysctl -w fs.file-max=300000
Backing up Package Security Manager#
Follow these steps to back up your instance of Package Security Manager:
Open a terminal and connect to your instance of Package Security Manager.
Enter your installer directory.
Create a backup of the
docker-compose.ymland.envfiles. These files contain your server’s custom configurations and are overwritten during reinstallation.Using your preferred file editor, open the
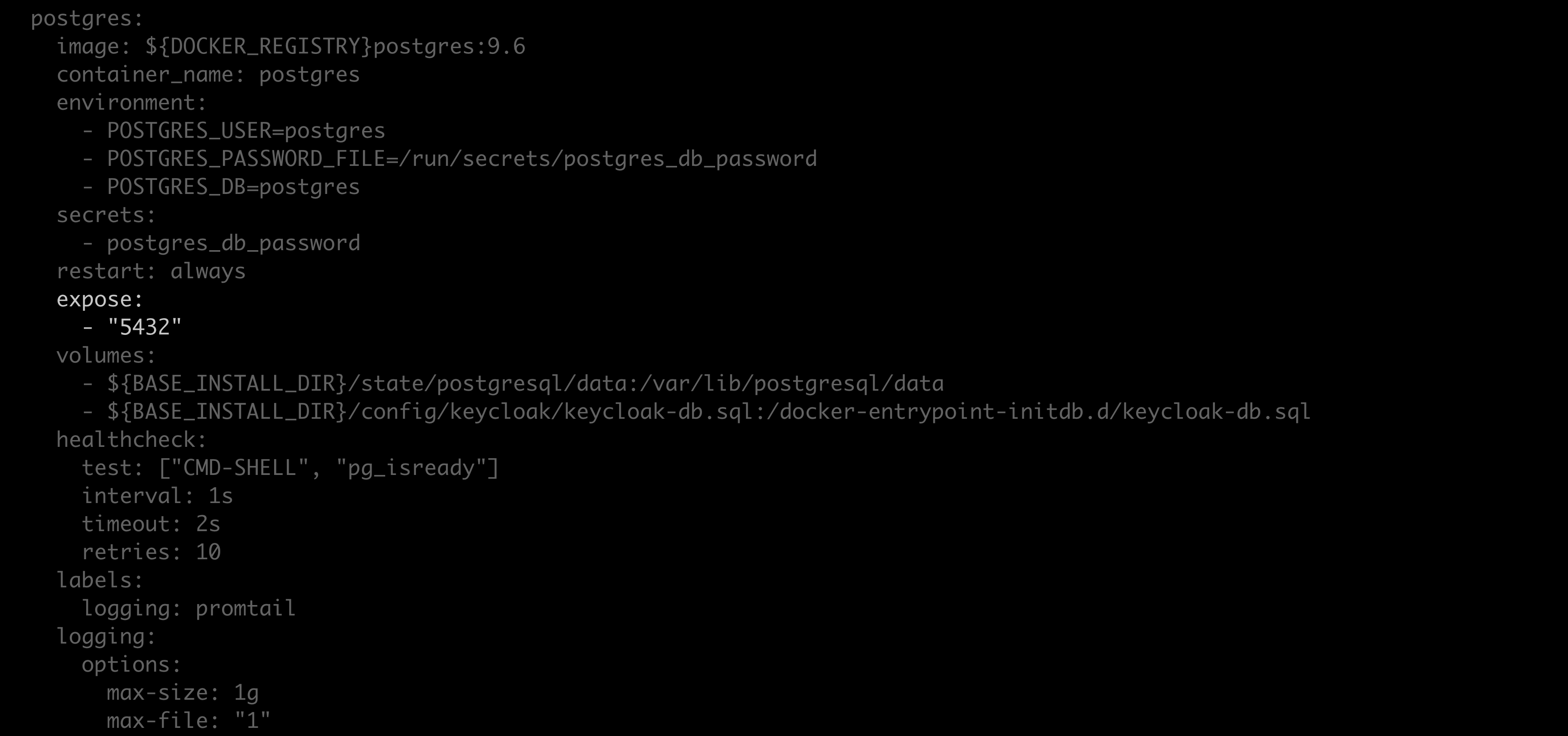
docker-compose.ymlfile.Locate the
Postgres: expose:section of the file.Replace
exposewithports, and replace"5432"with"5432:5432".Save your work and close the file.
Restart your containers by running the following command:
docker compose up --detach
Run the following command from the install directory:
# Replace <POSTGRES_PASSWORD> with your postgres password ./repo-tools backup --database-uri postgresql://postgres:<POSTGRES_PASSWORD>@localhost:5432/postgres --keycloak-database-uri postgresql://postgres:<POSTGRES_PASSWORD>@localhost:5432/keycloak --blob-dir /opt/anaconda/repo/state/internal/blobs/ > repo.backup.zip
Note
You can find your postgres password here:
<BASE_INSTALL_DIR>/config/postgres/postgres_db_password.txt. By default, the<BASE_INSTALL_DIR>is/opt/anaconda/repo.Save the
repo.backup.zipfile to a secure location.Overwrite the modified
docker-compose.ymlwith the backup copy to restore your custom configurations.Overwrite the modified
.envfile with the backup copy to restore your custom environmental variables.Restart your containers by running the following command:
docker compose up --detach
Restoring Package Security Manager#
Follow these steps to restore your instance of Package Security Manager:
Open a terminal and connect to your instance of Package Security Manager.
Enter your installer directory (
ate-installer-*).Using your preferred file editor, open the
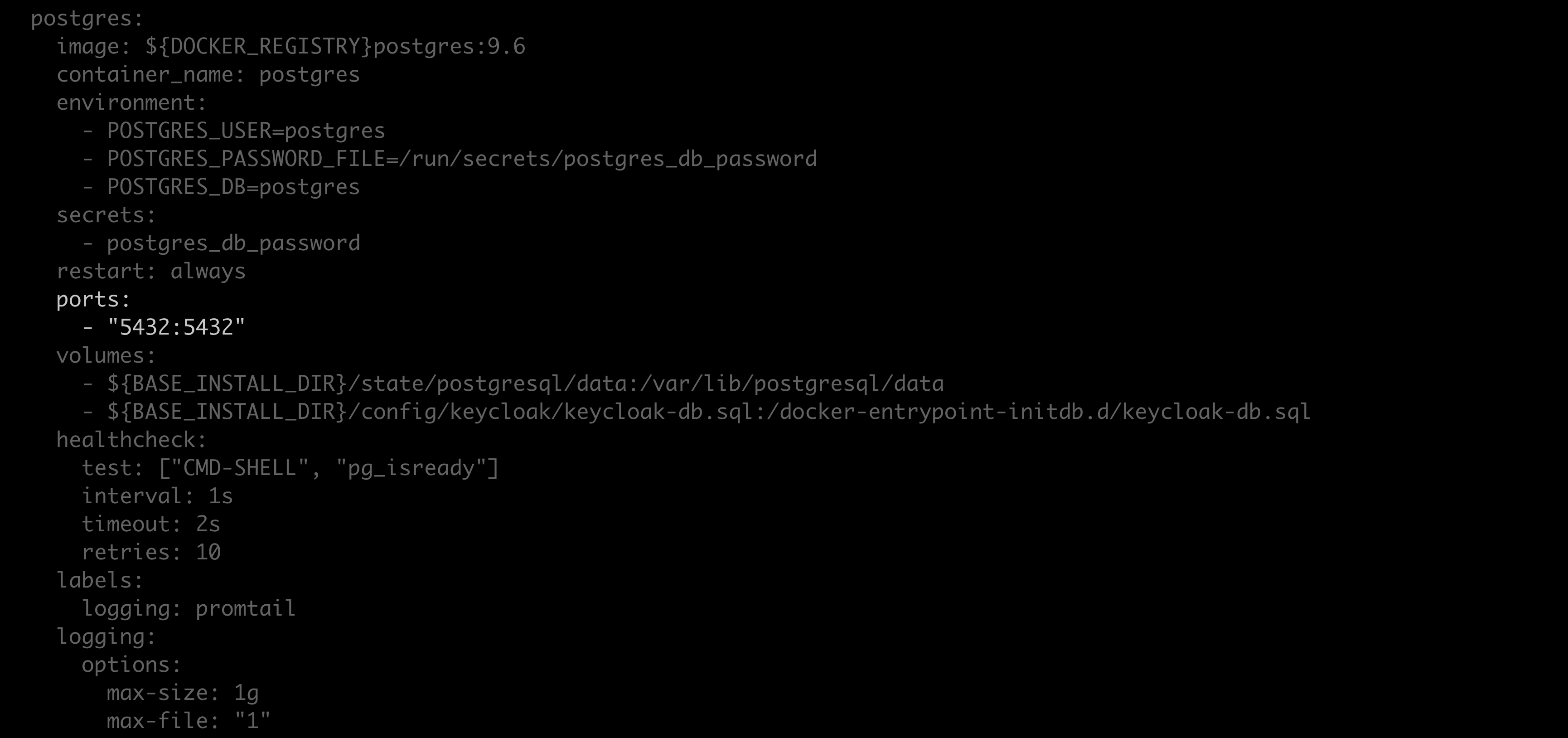
docker-compose.ymlfile.Locate the
Postgres: expose:section of the file.Replace
exposewithports, and replace"5432"with"5432:5432".Save your work and close the file.
Restart your containers by running the following command:
docker compose up --detach
Copy the
repo.backup.zipfile to your Package Security Manager’s server.Run the following command from the install directory:
# Replace <POSTGRES_PASSWORD> with your postgres password ./repo-tools restore repo.backup.zip --database-uri postgresql://postgres:<POSTGRES_PASSWORD>@localhost:5432/postgres --keycloak-database-uri postgresql://postgres:<POSTGRES_PASSWORD>@localhost:5432/keycloak --blob-dir /opt/anaconda/repo/state/internal/blobs/
Note
You can find your postgres password here:
<BASE_INSTALL_DIR>/config/postgres/postgres_db_password.txt. By default, the<BASE_INSTALL_DIR>is/opt/anaconda/repo.Overwrite the modified
docker-compose.ymlwith the backup copy to restore your configurations.Using your preferred file editor, open the new installation’s
.envfile.Manually edit the new installation’s
.envfile to include any custom environmental variables from the backup.envfile.Caution
Do not overwrite the new
.envfile with the backup. The new.envfile contains passwords that are required for proper functionality.Replace these values in the
.envfile with the values from the backup file:REPO_TOKEN_CLIENT_SECRET REPO_KEYCLOAK_SYNC_CLIENT_SECRET
Run the following command in the install directory:
docker compose up --detach repo_api