Standard installation#
This topic provides guidance on installing Package Security Manager and verifying your installation.
Note
These instructions assume that you have completed environment preparation.
Installing Package Security Manager#
Download your installer by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER_LOCATION> with the provided installer URL curl -O <INSTALLER_LOCATION>
Caution
If you do not have root access, you must add yourself to the docker group by running the following command before you install:
# Replace <USERNAME> with your Anaconda username usermod -a -G docker <USERNAME>
Run one of the following installation commands. Choose the command that corresponds with your setup.
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the installer you just downloaded # Replace <FQDN> with the fully qualified domain name of your Package Security Manager instance sudo bash <INSTALLER> --keep -- --domain <FQDN> --default-user anaconda 2>&1 | tee as.install.output
Note
To include Grafana monitoring dashboards in your installation of Package Security Manager, add the following argument to your installation command:
--grafana-monitor-stack
If you are using TLS/SSL certificates, run this command to install Package Security Manager:
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the installer you just downloaded # Replace <FQDN> with the fully qualified domain name of your Package Security Manager instance # Replace <PATH_TO_CERT> with the path to your TLS/SSL cert # Replace <PATH_TO_KEY> with the path to your TLS/SSL key sudo bash <INSTALLER> --keep -- --domain <FQDN> --tls-cert <PATH_TO_CERT> --tls-key <PATH_TO_KEY> --default-user anaconda 2>&1 | tee as.install.output
Note
To include Grafana monitoring dashboards in your installation of Package Security Manager, add the following argument to your installation command:
--grafana-monitor-stack
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the installer file you just downloaded # Replace <FQDN> with the fully qualified domain name of your Package Security Manager instance # Replace <PATH_TO_CERT> with the path to your TLS/SSL cert # Replace <PATH_TO_KEY> with the path to your TLS/SSL key # Replace <EXTERNAL_PG> with your external Postgres host IP4 address # Replace <ASSIGNED_PORT> with the port assigned to Postgres (default is 5432) # Replace <PSM_PASSWORD> with the password you established during setup bash <INSTALLER> --keep -- --domain <FQDN> --tls-cert <PATH_TO_CERT> --tls-key <PATH_TO_KEY> --default-user anaconda --pg-host <EXTERNAL_PG> --pg-port <ASSIGNED_PORT> --pg-user anaconda --pg-password <PSM_PASSWORD> 2>&1 | tee as.install.output
Note
To include Grafana monitoring dashboards in your installation of Package Security Manager, add the following argument to your installation command:
--grafana-monitor-stack
Allow the installation to fail, then clean itself up.
Enter the
ate-installer-*directory that was created from the installation process.Using your preferred file editor, open the
.envfile and update thePOSTGRES_URIvariable to point to the database created during setup.For example, your current connection string might look something like this:
POSTGRES_URI=postgresql://anaconda:<PSM_PASSWORD>@<EXTERNAL_PG>:5432/postgres
Update the connection string to use the database for the user you created and are using for installation as shown:
POSTGRES_URI=postgresql://anaconda:<PSM_PASSWORD>@<EXTERNAL_PG>:5432/anaconda
Save your work and close the file.
Using your preferred file editor, open the
docker-compose.ymlfile, and find thekeycloak:section.Update the
KC_DB_PASSWORDenvironment variable to the password you established for thekeycloakuser during environment prep.The correct formatting is shown below:
# Replace <KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD> with the password you established during setup - KC_DB_PASSWORD=<KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD>
Save your work and close the file.
Restart your containers by running the following command:
docker composer up -d
# Replace <INSTALLER> with the installer file you just downloaded # Replace <FQDN> with the fully qualified domain name of your Package Security Manager instance # Replace <PATH_TO_CERT> with the path to your TLS/SSL cert # Replace <PATH_TO_KEY> with the path to your TLS/SSL key # Replace <EXTERNAL_PG/RD_INSTANCE_IP4> with your external instance IP4 address (in both locations) # Replace <ASSIGNED_PORT> with the port used for communication # Replace <POSTGRES_USERID> with your postgres user ID # Replace <POSTGRES_PASSWORD> with your postgres password chmod +x <INSTALLER> bash <INSTALLER> --keep -- --domain <FQDN> --tls-cert <PATH_TO_CERT> --tls-key <PATH_TO_KEY> -e redis://<EXTERNAL_PG/RD_INSTANCE_IP4> -h <EXTERNAL_PG/RD_INSTANCE_IP4> -p <ASSIGNED_PORT> -u <POSTGRES_USERID> -pw <POSTGRES_PASSWORD> --default-user anaconda -y 2>&1 | tee as.install.output
Note
To include Grafana monitoring dashboards in your installation of Package Security Manager, add the following argument to your installation command:
--grafana-monitor-stack
The installation process creates three distinct user profiles: one for administrating Package Security Manager, one for administrating Keycloak, and one for accessing Prometheus. Login credentials for these profiles are shown during the installer output. Use these credentials for your initial logins, and update them as soon as possible.
Example output
KeyCloak admin user: 'admin' KeyCloak admin password: 'B1EpU33Wasdfh0Z64LL767cD' Updating Keycloak settings ... Default user: 'anaconda' password: '8aZ6302Ssd34ge415Ld97I' Prometheus admin user: username=admin Generated password for prometheus password=34ab35y63CUJak6asdf2Am7z40z7lhG8Note
The Prometheus password cannot currently be updated. Save your password somewhere secure!
Note
The installer directory contains both the installation script (install.sh) and the docker-compose.yml file, which defines how Package Security Manager services are run.
By default, /opt/anaconda/repo is the file path for the installation folder. You can either create the folder manually by assigning write access to the current user, or use the -b (--base-install-dir) parameter to specify the folder for your installation.
Warning
Never delete the directory containing the docker-compose.yml and .env files.
Verifying your installation#
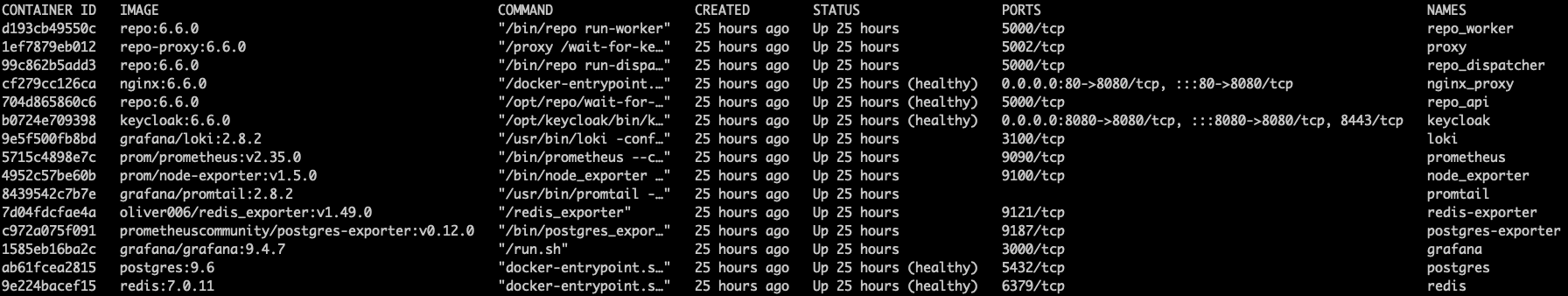
Services are one-to-one to containers. Therefore, verifying that all major containers are up and not restarting or failing is a good first step.
Return to your terminal and run the following command:
Verify that the following containers appear with a
STATUSofUp(not stuck in a restart loop) in the output:repo_api repo_worker repo_dispatcher proxy nginx_proxy keycloak redis postgres
These containers should always be running. However, you might see additional containers, depending on the phase of installation or your initial configuration choices:
Additional containers
loki grafana promtail prometheus node_exporter redis-exporter postgres-exporter
Open a browser and navigate to the domain that you supplied when executing the installer. If you are able to successfully authenticate and are asked for a license, Package Security Manager has installed successfully.
Advanced options#
Further installation options can be seen by running the following command:
# Replace <INSTALLER> with your installer file
./<INSTALLER>/install.sh --help
This will present you with the following list of possible arguments:
Arguments (shorthand) |
Arguments (longhand) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Docker registry, |
|
|
Postgresql host (default is on internal Postgres instance) |
|
|
Postgresql port number |
|
|
Postgresql username |
|
|
Postgresql password (will set the internal Postgres instance password) |
|
|
Redis URL (default is an internal Redis instance) |
|
|
External domain (or IP address) of host system |
|
|
Path to TLS certification file for optionally configuring HTTPS (includes the host certificate and all intermediate certificates, but not the Root CA) |
|
|
Path to TLS key file for optionally configuring HTTPS |
|
Default user name |
|
|
Path to custom CA certification, which should be respected |
|
|
For air-gapped environments provide a custom source for CVE data |
|
|
Previous install folder |
|
|
|
Don’t load Docker images |
|
|
Answer yes to all prompts |
|
Print help text |